Jenkins
Our Jenkins integration allows you to import jobs, builds, and users from your Jenkins environment into Port, according to your mapping and definitions.
Common use cases
- Map
jobs,builds, andusersin your Jenkins environment. - Watch for object changes (create/update/delete) in real-time, and automatically apply the changes to your entities in Port.
Prerequisites
To install the integration, you need a Kubernetes cluster that the integration's container chart will be deployed to.
Please make sure that you have kubectl and helm installed on your machine, and that your kubectl CLI is connected to the Kubernetes cluster where you plan to install the integration.
If you are having trouble installing this integration, please refer to these troubleshooting steps.
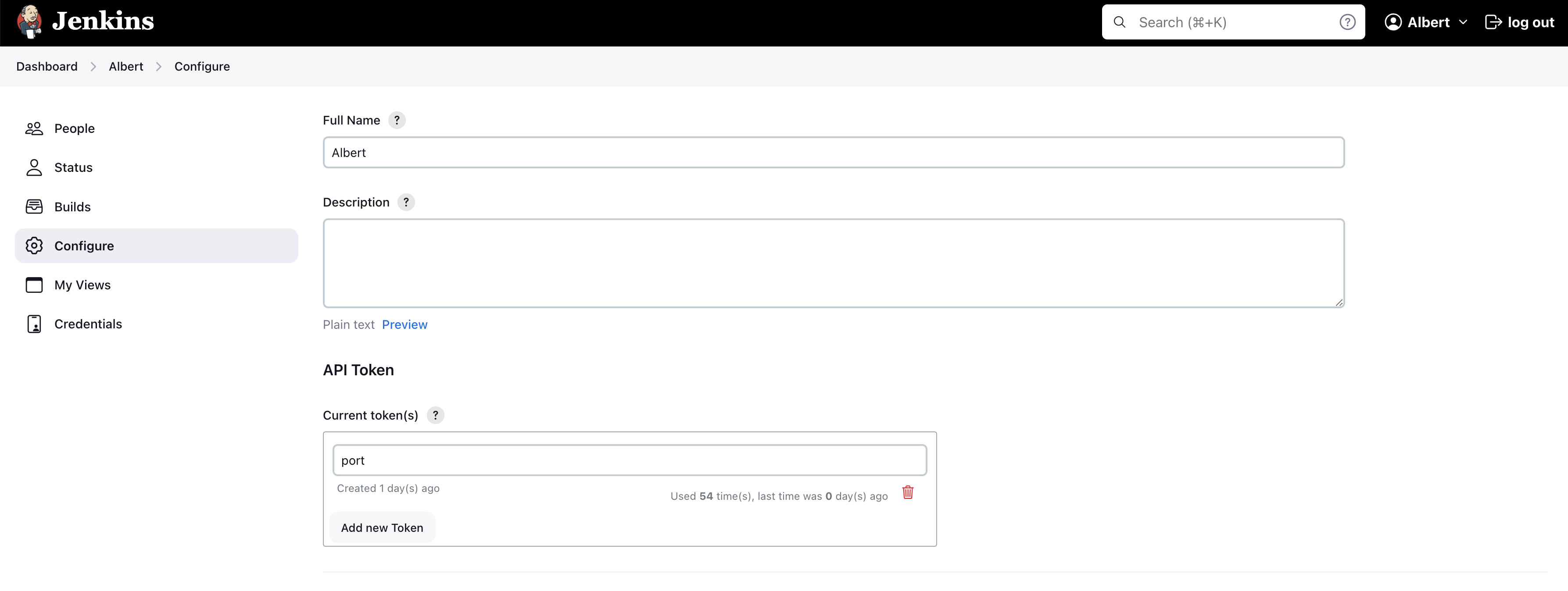
To generate a token for authenticating the Jenkins API calls:
- In the Jenkins banner frame, click your user name to open the user menu.
- Navigate to Your Username > Configure > API Token.
- Click Add new Token.
- Click Generate.
- Copy the API token that is generated to use as the
JENKINS_TOKEN.
Recent Jenkins versions (2.452 and above) no longer include the "People" view by default. This view is essential for providing the user information API that will be queried by the integration.
To install the plugin:
- In Jenkins, navigate to Manage Jenkins -> Plugins.
- Search for and install the "People View" plugin.
Installation
Choose one of the following installation methods:
- Real Time & Always On
- Scheduled
Using this installation option means that the integration will be able to update Port in real time using webhooks.
This table summarizes the available parameters for the installation. Set them as you wish in the script below, then copy it and run it in your terminal:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
port.clientId | Your port client id (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
port.clientSecret | Your port client secret (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
port.baseUrl | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
integration.identifier | Change the identifier to describe your integration | ✅ |
integration.type | The integration type | ✅ |
integration.eventListener.type | The event listener type | ✅ |
integration.secrets.jenkinsUser | The Jenkins username | ✅ |
integration.secrets.jenkinsToken | The Jenkins password or token | ✅ |
integration.config.jenkinsHost | The Jenkins host | ✅ |
integration.config.appHost | The host of the Port Ocean app. Used to set up the integration endpoint as the target for webhooks created in Jenkins | ❌ |
scheduledResyncInterval | The number of minutes between each resync | ❌ |
initializePortResources | Default true, When set to true the integration will create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
- Helm
- ArgoCD
To install the integration using Helm, run the following command:
helm repo add --force-update port-labs https://port-labs.github.io/helm-charts
helm upgrade --install my-jenkins-integration port-labs/port-ocean \
--set port.clientId="PORT_CLIENT_ID" \
--set port.clientSecret="PORT_CLIENT_SECRET" \
--set port.baseUrl="https://api.getport.io" \
--set initializePortResources=true \
--set scheduledResyncInterval=120 \
--set integration.identifier="my-jenkins-integration" \
--set integration.type="jenkins" \
--set integration.eventListener.type="POLLING" \
--set integration.secrets.jenkinsUser="JENKINS_USER" \
--set integration.secrets.jenkinsToken="JENKINS_TOKEN" \
--set integration.config.jenkinsHost="JENKINS_HOST"
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port, available at https://app.getport.io, your Port API URL is
https://api.getport.io - If you use the US region of Port, available at https://app.us.getport.io, your Port API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io
To install the integration using ArgoCD, follow these steps:
- Create a
values.yamlfile inargocd/my-ocean-jenkins-integrationin your git repository with the content:
Remember to replace the placeholders for JENKINS_USER, JENKINS_TOKEN and JENKINS_HOST.
initializePortResources: true
scheduledResyncInterval: 120
integration:
identifier: my-ocean-jenkins-integration
type: jenkins
eventListener:
type: POLLING
config:
jenkinsHost: JENKINS_HOST
secrets:
jenkinsUser: JENKINS_USER
jenkinsToken: JENKINS_TOKEN
- Install the
my-ocean-jenkins-integrationArgoCD Application by creating the followingmy-ocean-jenkins-integration.yamlmanifest:
Remember to replace the placeholders for YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_ID YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_SECRET and YOUR_GIT_REPO_URL.
Multiple sources ArgoCD documentation can be found here.
ArgoCD Application
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-ocean-jenkins-integration
namespace: argocd
spec:
destination:
namespace: my-ocean-jenkins-integration
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
sources:
- repoURL: 'https://port-labs.github.io/helm-charts/'
chart: port-ocean
targetRevision: 0.1.14
helm:
valueFiles:
- $values/argocd/my-ocean-jenkins-integration/values.yaml
parameters:
- name: port.clientId
value: YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_ID
- name: port.clientSecret
value: YOUR_PORT_CLIENT_SECRET
- name: port.baseUrl
value: https://api.getport.io
- repoURL: YOUR_GIT_REPO_URL
targetRevision: main
ref: values
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port, available at https://app.getport.io, your Port API URL is
https://api.getport.io - If you use the US region of Port, available at https://app.us.getport.io, your Port API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io
- Apply your application manifest with
kubectl:
kubectl apply -f my-ocean-jenkins-integration.yaml
- GitHub
- Jenkins
- Azure Devops
- GitLab
This workflow will run the Jenkins integration once and then exit, this is useful for scheduled ingestion of data.
If you want the integration to update Port in real time using webhooks you should use the Real Time & Always On installation option
Make sure to configure the following Github Secrets:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER | The Jenkins Username | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN | The Jenkins Token | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST | The Jenkins Host | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Provide a unique identifier for your integration. If not provided, the default identifier will be used. | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for jenkins-integration.yml workflow file:
name: Jenkins Exporter Workflow
# This workflow responsible for running Jenkins exporter.
on:
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
run-integration:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: port-labs/ocean-sail@v1
with:
type: 'jenkins'
port_client_id: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID }}
port_client_secret: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET }}
port_base_url: https://api.getport.io
config: |
jenkins_host: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST }}
jenkins_user: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER }}
jenkins_token: ${{ secrets.OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN }}
This pipeline will run the Jenkins integration once and then exit, this is useful for scheduled ingestion of data.
Your Jenkins agent should be able to run docker commands.
If you want the integration to update Port in real time using webhooks you should use the Real Time & Always On installation option.
Make sure to configure the following Jenkins Credentials
of Secret Text type:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER | The Jenkins Username | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN | The Jenkins Token | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST | The Jenkins Host | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Provide a unique identifier for your integration. If not provided, the default identifier will be used. | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for Jenkinsfile groovy pipeline file:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Run Jenkins Integration') {
steps {
script {
withCredentials([
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER', variable: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN', variable: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST', variable: 'OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID', variable: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID'),
string(credentialsId: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET', variable: 'OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET'),
]) {
sh('''
#Set Docker image and run the container
integration_type="jenkins"
version="latest"
image_name="ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-${integration_type}:${version}"
docker run -i --rm --platform=linux/amd64 \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$image_name
exit $?
''')
}
}
}
}
}
}
This pipeline will run the Jenkins integration once and then exit, this is useful for scheduled ingestion of data.
Your Azure Devops agent should be able to run docker commands. Learn more about agents here.
If you want the integration to update Port in real time using webhooks you should use the Real Time & Always On installation option.
Variable groups store values and secrets you'll use in your pipelines across your project. Learn more
Setting Up Your Credentials
- Create a Variable Group: Name it port-ocean-credentials. Store the required variables from the table.
- Authorize Your Pipeline:
- Go to "Library" -> "Variable groups."
- Find port-ocean-credentials and click on it.
- Select "Pipeline Permissions" and add your pipeline to the authorized list.

| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER | The Jenkins Username | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN | The Jenkins Token | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST | The Jenkins Host | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Provide a unique identifier for your integration. If not provided, the default identifier will be used. | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for jenkins-integration.yml pipeline file:
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: "ubuntu-latest"
variables:
- group: port-ocean-credentials
steps:
- script: |
# Set Docker image and run the container
integration_type="jenkins"
version="latest"
image_name="ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-$integration_type:$version"
docker run -i --rm \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER=$(OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER) \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN=$(OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN) \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST=$(OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$(OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$(OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET) \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$image_name
exit $?
displayName: 'Ingest Data into Port'
This workflow will run the Jenkins integration once and then exit, this is useful for scheduled ingestion of data.
If you want the integration to update Port in real time using webhooks you should use the Real Time & Always On installation option.
Make sure to configure the following GitLab variables:
| Parameter | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER | The Jenkins Username | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN | The Jenkins Token | ✅ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST | The Jenkins Host | ✅ |
OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES | Default true, When set to false the integration will not create default blueprints and the port App config Mapping | ❌ |
OCEAN__INTEGRATION__IDENTIFIER | Provide a unique identifier for your integration. If not provided, the default identifier will be used. | ❌ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID | Your port client id (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET | Your port client secret (Get the credentials) | ✅ |
OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL | Your Port API URL - https://api.getport.io for EU, https://api.us.getport.io for US | ✅ |
Here is an example for .gitlab-ci.yml pipeline file:
default:
image: docker:24.0.5
services:
- docker:24.0.5-dind
before_script:
- docker info
variables:
INTEGRATION_TYPE: jenkins
VERSION: latest
stages:
- ingest
ingest_data:
stage: ingest
variables:
IMAGE_NAME: ghcr.io/port-labs/port-ocean-$INTEGRATION_TYPE:$VERSION
script:
- |
docker run -i --rm --platform=linux/amd64 \
-e OCEAN__EVENT_LISTENER='{"type":"ONCE"}' \
-e OCEAN__INITIALIZE_PORT_RESOURCES=true \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_USER \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_TOKEN \
-e OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST=$OCEAN__INTEGRATION__CONFIG__JENKINS_HOST \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_ID \
-e OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET=$OCEAN__PORT__CLIENT_SECRET \
-e OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL='https://api.getport.io' \
$IMAGE_NAME
rules: # Run only when changes are made to the main branch
- if: '$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "main"'
The baseUrl, port_region, port.baseUrl, portBaseUrl, port_base_url and OCEAN__PORT__BASE_URL parameters are used to select which instance or Port API will be used.
Port exposes two API instances, one for the EU region of Port, and one for the US region of Port.
- If you use the EU region of Port, available at https://app.getport.io, your Port API URL is
https://api.getport.io - If you use the US region of Port, available at https://app.us.getport.io, your Port API URL is
https://api.us.getport.io
For advanced configuration such as proxies or self-signed certificates, click here.
Ingesting Jenkins objects
The Jenkins integration uses a YAML configuration to describe the process of loading data into the developer portal.
Here is an example snippet from the config which demonstrates the process for getting job data from Jenkins:
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: job
selector:
query: "true"
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .url | split("://")[1] | sub("^.*?/"; "") | gsub("%20"; "-") | gsub("/"; "-") | .[:-1]
title: .fullName
blueprint: '"jenkinsJob"'
properties:
jobName: .name
url: .url
jobStatus: '{"notbuilt": "created", "blue": "passing", "red": "failing"}[.color]'
timestamp: .time
The integration makes use of the JQ JSON processor to select, modify, concatenate, transform and perform other operations on existing fields and values from Jenkins's API events.
Configuration structure
The integration configuration determines which resources will be queried from Jenkins, and which entities and properties will be created in Port.
-
The root key of the integration configuration is the
resourceskey:resources:
- kind: job
selector:
... -
The
kindkey is a specifier for a Jenkins object:resources:
- kind: job
selector:
... -
The
selectorand thequerykeys allow you to filter which objects of the specifiedkindwill be ingested into your software catalog:resources:
- kind: job
selector:
query: "true" # JQ boolean expression. If evaluated to false - this object will be skipped.
port: -
The
port,entityand themappingskeys are used to map the Jenkins object fields to Port entities. To create multiple mappings of the same kind, you can add another item in theresourcesarray;resources:
- kind: job
selector:
query: "true"
port:
entity:
mappings: # Mappings between one Jenkins object to a Port entity. Each value is a JQ query.
identifier: .url | split("://")[1] | sub("^.*?/"; "") | gsub("%20"; "-") | gsub("/"; "-") | .[:-1]
title: .fullName
blueprint: '"jenkinsJob"'
properties:
jobName: .name
url: .url
jobStatus: '{"notbuilt": "created", "blue": "passing", "red": "failing"}[.color]'
timestamp: .time
- kind: job # In this instance job is mapped again with a different filter
selector:
query: '.name == "MyJobName"'
port:
entity:
mappings: ...Blueprint keyNote the value of the
blueprintkey - if you want to use a hardcoded string, you need to encapsulate it in 2 sets of quotes, for example use a pair of single-quotes (') and then another pair of double-quotes (")
Ingest data into Port
To ingest Jenkins objects using the integration configuration, you can follow the steps below:
- Go to the DevPortal Builder page.
- Select a blueprint you want to ingest using Jenkins.
- Choose the Ingest Data option from the menu.
- Select Jenkins under the CI/CD category.
- Modify the configuration according to your needs.
- Click
Resync.
Examples
Examples of blueprints and the relevant integration configurations:
Job
Job blueprint
{
"identifier": "jenkinsJob",
"description": "This blueprint represents a job in Jenkins",
"title": "Jenkins Job",
"icon": "Jenkins",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"jobName": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Job Name"
},
"jobStatus": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Job Status",
"enum": [
"created",
"unknown",
"passing",
"failing"
],
"enumColors": {
"passing": "green",
"created": "darkGray",
"failing": "red",
"unknown": "orange"
}
},
"timestamp": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time",
"title": "Timestamp",
"description": "Last updated timestamp of the job"
},
"url": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Project URL"
},
"parentJob": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Parent Job"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Integration configuration
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: job
selector:
query: "true"
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .url | split("://")[1] | sub("^.*?/"; "") | gsub("%20"; "-") | gsub("/"; "-") | .[:-1]
title: .fullName
blueprint: '"jenkinsJob"'
properties:
jobName: .name
url: .url
jobStatus: '{"notbuilt": "created", "blue": "passing", "red": "failing"}[.color]'
timestamp: .time
parentJob: .__parentJob
Build
Build blueprint
{
"identifier": "jenkinsBuild",
"description": "This blueprint represents a build event from Jenkins",
"title": "Jenkins Build",
"icon": "Jenkins",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"buildStatus": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Build Status",
"enum": [
"SUCCESS",
"FAILURE",
"UNSTABLE"
],
"enumColors": {
"SUCCESS": "green",
"FAILURE": "red",
"UNSTABLE": "yellow"
}
},
"buildUrl": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Build URL",
"description": "URL to the build"
},
"timestamp": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time",
"title": "Timestamp",
"description": "Last updated timestamp of the build"
},
"buildDuration": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Build Duration",
"description": "Duration of the build"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {
"previousBuildStatus": {
"title": "Previous Build Status",
"path": "previousBuild.buildStatus"
}
},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"parentJob": {
"title": "Jenkins Job",
"target": "jenkinsJob",
"required": false,
"many": false
},
"previousBuild": {
"title": "Previous Build",
"target": "jenkinsBuild",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
}
Integration configuration
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: build
selector:
query: "true"
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .url | split("://")[1] | sub("^.*?/"; "") | gsub("%20"; "-") | gsub("/"; "-") | .[:-1]
title: .displayName
blueprint: '"jenkinsBuild"'
properties:
buildStatus: .result
buildUrl: .url
buildDuration: .duration
timestamp: '.timestamp / 1000 | todate'
relations:
parentJob: .url | split("://")[1] | sub("^.*?/"; "") | gsub("%20"; "-") | gsub("/"; "-") | .[:-1] | gsub("-[0-9]+$"; "")
previousBuild: .previousBuild.url | split("://")[1] | sub("^.*?/"; "") | gsub("%20"; "-") | gsub("/"; "-") | .[:-1]
User
User blueprint
{
"identifier": "jenkinsUser",
"description": "This blueprint represents a jenkins user",
"title": "Jenkins User",
"icon": "Jenkins",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"url": {
"type": "string",
"title": "URL",
"format": "url"
},
"lastUpdateTime": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time",
"title": "Last Update",
"description": "Last updated timestamp of the user"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
Integration configuration
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
deleteDependentEntities: true
resources:
- kind: user
selector:
query: "true"
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .user.id
title: .user.fullName
blueprint: '"jenkinsUser"'
properties:
url: .user.absoluteUrl
lastUpdateTime: if .lastChange then (.lastChange/1000) else now end | strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ")
Let's Test It
This section includes a sample response data from Jenkins. In addition, it includes the entity created from the resync event based on the Ocean configuration provided in the previous section.
Payload
Here is an example of the payload structure from Jenkins:
Job response data
{
"_class" : "hudson.model.FreeStyleProject",
"displayName" : "Hello Job",
"fullName" : "Hello Job",
"name" : "Hello Job",
"url" : "http://localhost:8080/job/Hello%20Job/",
"buildable" : true,
"builds" : [
{
"_class" : "hudson.model.FreeStyleBuild",
"displayName" : "#2",
"duration" : 221,
"fullDisplayName" : "Hello Job #2",
"id" : "2",
"number" : 2,
"result" : "SUCCESS",
"timestamp" : 1700569094576,
"url" : "http://localhost:8080/job/Hello%20Job/2/"
},
{
"_class" : "hudson.model.FreeStyleBuild",
"displayName" : "#1",
"duration" : 2214,
"fullDisplayName" : "Hello Job #1",
"id" : "1",
"number" : 1,
"result" : "SUCCESS",
"timestamp" : 1700567994163,
"url" : "http://localhost:8080/job/Hello%20Job/1/"
}
],
"color" : "blue"
}
Build response data
{
"_class" : "hudson.model.FreeStyleBuild",
"displayName" : "#2",
"duration" : 221,
"fullDisplayName" : "Hello Job #2",
"id" : "2",
"number" : 2,
"result" : "SUCCESS",
"timestamp" : 1700569094576,
"url" : "http://localhost:8080/job/Hello%20Job/2/"
}
User response data
{
"user" : {
"absoluteUrl" : "http://localhost:8080/user/admin",
"fullName" : "admin",
"description" : "System Administrator",
"id" : "admin"
},
"lastChange" : 1700569094576
}
Mapping Result
The combination of the sample payload and the Ocean configuration generates the following Port entity:
Job entity
{
"identifier": "hello-job",
"title": "Hello Job",
"blueprint": "jenkinsJob",
"properties": {
"jobName": "Hello Job",
"url": "http://localhost:8080/job/Hello%20Job/",
"jobStatus": "passing",
"timestamp": "2023-09-08T14:58:14Z"
},
"relations": {},
"createdAt": "2023-12-18T08:37:21.637Z",
"createdBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW",
"updatedAt": "2023-12-18T08:37:21.637Z",
"updatedBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW"
}
Build entity
{
"identifier": "hello-job-2",
"title": "Hello Job #2",
"blueprint": "jenkinsBuild",
"properties": {
"buildStatus": "SUCCESS",
"buildUrl": "http://localhost:8080/job/Hello%20Job/2/",
"buildDuration": 221,
"timestamp": "2023-09-08T14:58:14Z"
},
"relations": {
"parentJob": "hello-job"
},
"createdAt": "2023-12-18T08:37:21.637Z",
"createdBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW",
"updatedAt": "2023-12-18T08:37:21.637Z",
"updatedBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW"
}
User entity
{
"identifier": "admin",
"title": "admin",
"blueprint": "jenkinsUser",
"properties": {
"url": "http://localhost:8080/user/admin",
"lastUpdateTime": "2023-09-08T14:58:14Z"
},
"relations": {},
"createdAt": "2023-12-18T08:37:21.637Z",
"createdBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW",
"updatedAt": "2023-12-18T08:37:21.637Z",
"updatedBy": "hBx3VFZjqgLPEoQLp7POx5XaoB0cgsxW"
}